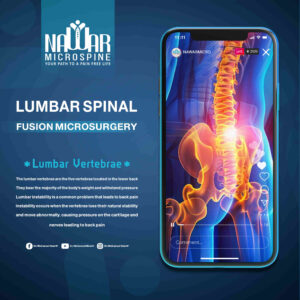
Lumbar Spine Fixation with the Microscope
The Precise and Safe Solution for Spinal Problems Lumbar spine fixation under the microscope is one of the most advanced, safe, and effective techniques for treating spinal conditions such as
A Revolution in Precision Spine Surgery
The field of spine surgery is witnessing continuous advancement, with one of the most significant breakthroughs being the use of the surgical microscope in lumbar canal decompression. This technique represents a true milestone, as it provides high-definition visualization that enables the surgeon to operate with exceptional precision and safety — minimizing complications and accelerating recovery.
This canal houses the nerve plexus responsible for lower limb movement, as well as nerves that control bladder function and sexual performance in men.
Lumbar canal stenosis occurs when the spinal canal becomes narrowed, putting pressure on the nerve plexus and impairing its function. Common causes include:
Lumbar canal stenosis occurs when the spinal canal becomes narrowed, putting pressure on the nerve plexus and impairing its function.
Unlike disc-related pain, which may persist even at rest, the symptoms of lumbar canal stenosis typically appear when standing or walking and improve when sitting or lying down.
Some cases require urgent medical evaluation, such as:
Diagnosis begins with a thorough assessment of symptoms and a detailed physical examination, supported by imaging studies such as MRI, CT scan, and standard X-rays.
For severe cases, microscopic decompression surgery is the most effective treatment. Mild to moderate cases may be managed with medication and physical therapy.
Surgery is recommended in cases of severe stenosis accompanied by one or more of the warning signs mentioned earlier, or when the patient can no longer perform daily activities such as walking or standing normally.
At Nawar MicroSpine Center, Dr. Mohamed Nawar uses the most advanced surgical systems, including:
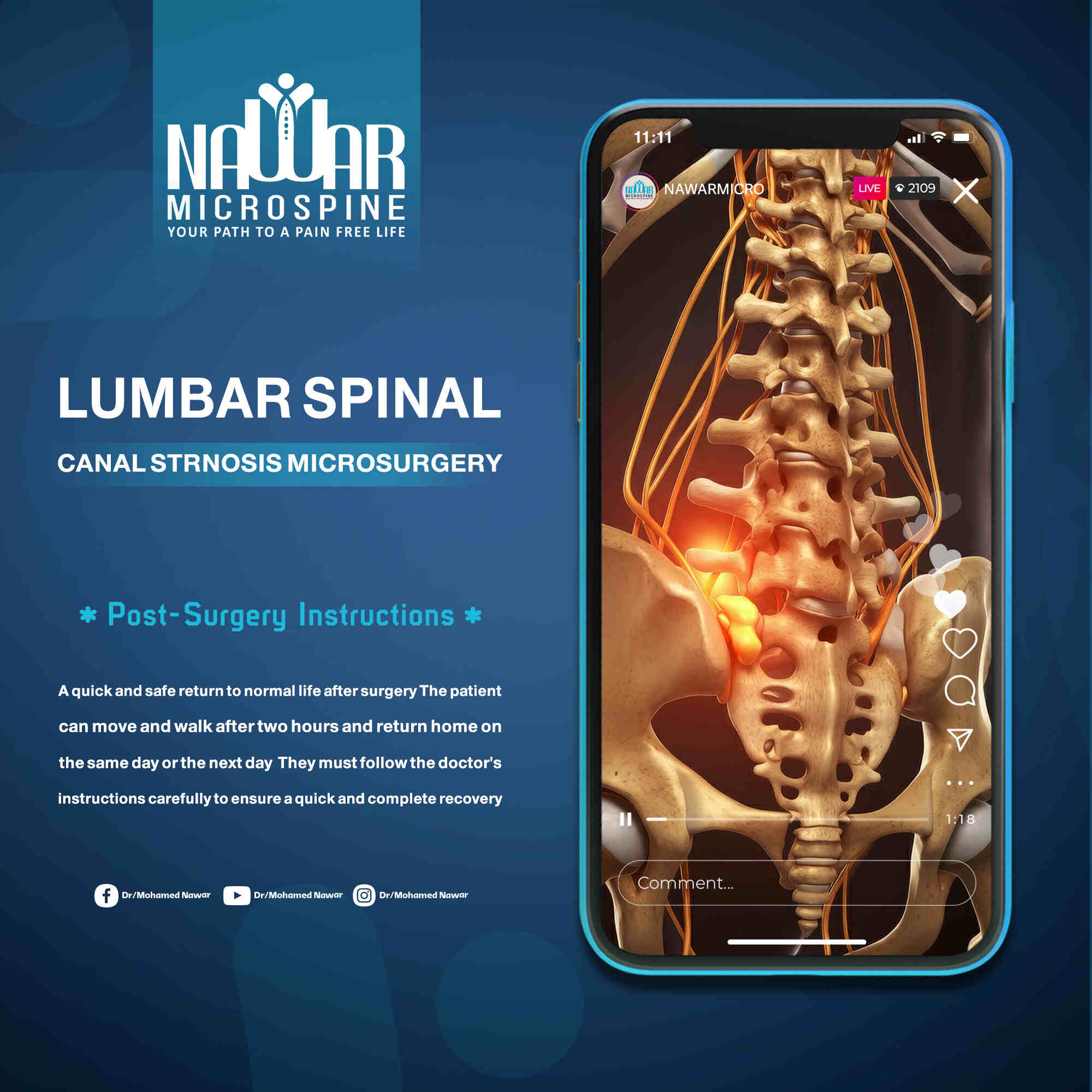
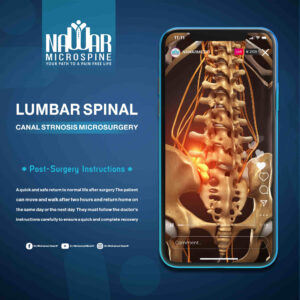
Patients can usually stand and walk within two hours after surgery and are discharged the same or next day. Strict adherence to medical instructions ensures a fast and complete recovery.
For more information about foot drop, you can watch the related educational videos.




If you experience any symptoms of lumbar spinal canal stenosis, you should consult a doctor immediately to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.


The Precise and Safe Solution for Spinal Problems Lumbar spine fixation under the microscope is one of the most advanced, safe, and effective techniques for treating spinal conditions such as

Preparations before spinal surgery Its steps and recovery instructions Spine surgery is a significant step in treating various back and neck conditions. It requires careful preparation, a clear understanding of
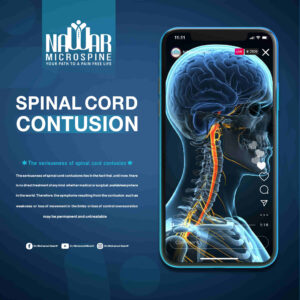
A Hidden Threat to the Spine A spinal cord contusion is one of the most serious spinal injuries, as it threatens a person’s ability to move and feel sensations. If
A Revolution in Precision Spine Surgery الرئيسية The field of spine surgery is witnessing continuous advancement, with one of the most significant breakthroughs being the use of the surgical microscope
Cervical spinal canal stenosis is one of the most common spinal problems, particularly among older adults. It causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the limbs and can lead to serious